Introduction to Virtual Commissioning
Learn the benefits of using Simumatik as a tool for Virtual Commissioning.
What is an Automated System?
An automated system is a combination of hardware and software that is built to work automatically, without the need of a human to perform all operations. Examples for automated systems can be found in most technological areas, mostly within production and process industries, but even outside of the industry they can be found as in elevators or smart home appliances. Virtual commissioning is mostly used within industrial automated systems, but can also be used in other areas.
In most examples of an automated system there is a controller that takes input parameters from a system or process and depending on the input parameters sets output parameters to control the system or process, as seen in the figure below
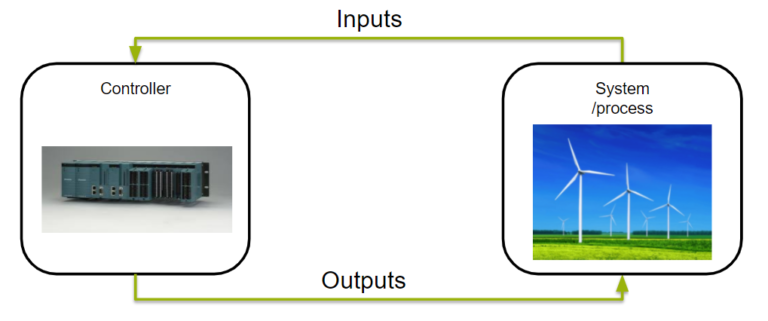
What is Commissioning?
A typical industrial automation system project consists of the following phases. Design, Engineering, Construction/Installation, Commissioning and Operation. Typically these project stages are done in a sequence, the commissioning cannot start until the installation is finished and the construction cannot start until the design is finished. The sequence can be displayed in the following way.
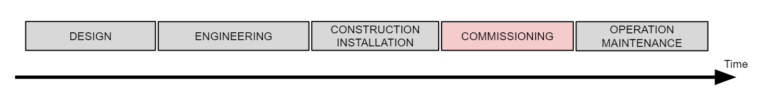
Commissioning:
- Refers to the process of checking, inspecting, and testing every component of the system, individually and as a system or subsystem.
- Guarantees operability in terms of performance, reliability, and safety.
- It is an essential factor for the fulfillment of the requirements and quality.
The main issues with commissioning are that it has a limited time, requires a lot of skills and resources, is the last step before acceptance (meaning it depends heavily on the previous project stages), and can often be very stressful for the engineers.
What is Virtual Commissioning?
The goal of Virtual Commissioning is to early validate and verify the automation project. But does not completely replace the real commissioning. It requires a virtual model of the system.
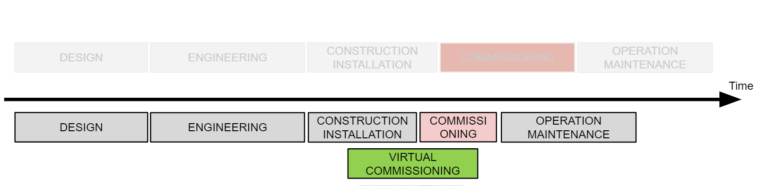
Benefits of using virtual commissioning:
- It reduces the risk of errors and increases the final quality of the system.
- Does not require the real system, so it can be performed in parallel to installation.
- Reduces stress and pressure for the engineers.
And the future?
Even if the concept of Virtual commissioning is quite old and has been around the last 2 decades, it present some challenges.
Mainly the knowledge and time required to build the actual models, and its costs against their benefits, its being discussed and questioned, which has been a key factor to adopt the technology. But nowadays, in the context of industry 4.0 the effort is being place on integrating the models through the entire process to increase their support to different phases and minimize the extra cost while increasing their benefits.
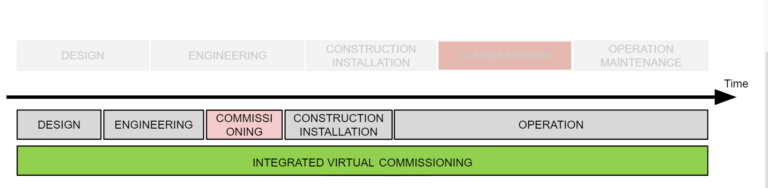
How Virtual Commissioning works?
By replacing the real system with an virtual system we can test and verify the software of the control system, either by using the real controller or an virtual controller (like a soft-PLC), as described in the image below.
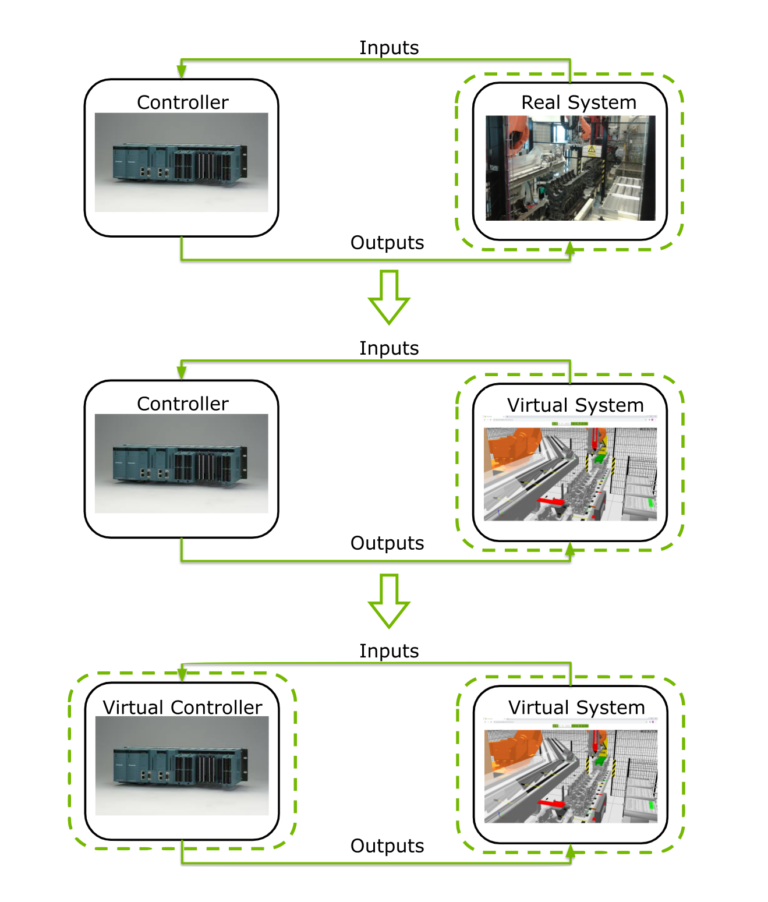
By replacing the real system with an virtual system we can test and verify the software of the control system, either by using the real controller or an virtual controller (like a soft-PLC), as described in the image below.
Simumatik offers a wide range of ready-to-use components to enable the modeling of different systems, for example, conveyors, robots, sensors, motors, pneumatic and hydraulic components, etc. By editing the existing components or creating new components in the Simumatik Component Editor there are unlimited possibilities to model your system. By combining these components in a Simumatik system, the physical system can be replicated.
Simumatik offers a wide range of ready-to-use components to enable the modeling of different systems, for example, conveyors, robots, sensors, motors, pneumatic and hydraulic components, etc. By editing the existing components or creating new components in the Simumatik Component Editor there are unlimited possibilities to model your system. By combining these components in a Simumatik system, the physical system can be replicated.
By connecting the Simumatik model to either a real or an emulated controller by the Simumatik Gateway, the software of the control system can be tested and verified. Simumatik offers a wide range of connections to different control systems, the gateway is also open source to enable the user to program interfaces between the Simumatik model and any 3rd party program.
The Simumatik model has different aspects of modeling.
- Visuals: How the component or system looks and appears in 3D space.
- Physics: The physical properties of a component, including material, collision shape, and kinematics. All used to replicate physical interaction using a physics engine.
- Interface: The connection points of a component, allowing it to be connected to other components or third-party software. These include electric, pneumatic and mechanical ports for example.
- Behavior: Components can be programmed to contain logic, bringing them to life. Component logic is programmed in the Python programming language.
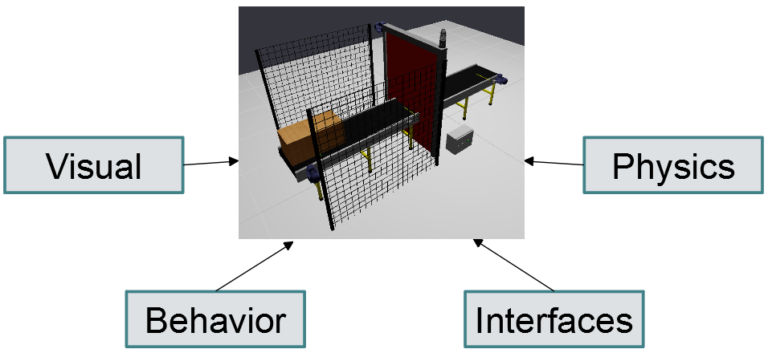
Each aspect, visual, physical, interfaces, and behavior, is flexible, and together they allow modeling almost any component you can imagine – from basic products, sensors and motors, to PLCs and robot controllers. However, not every component requires all aspects to be modeled.
Using Simumatik for Virtual Commissioning
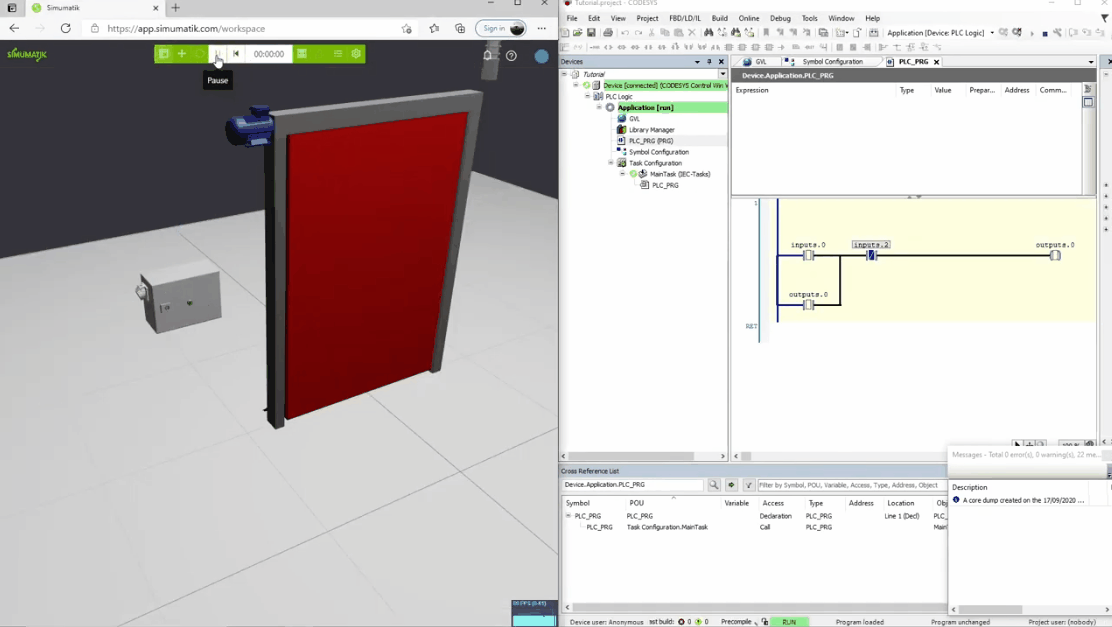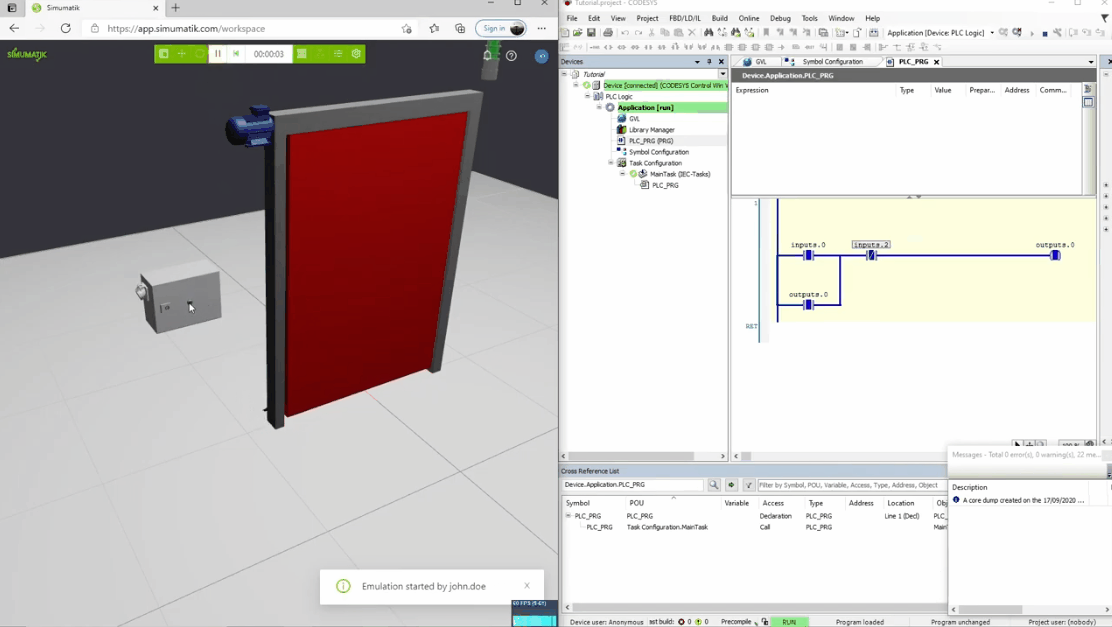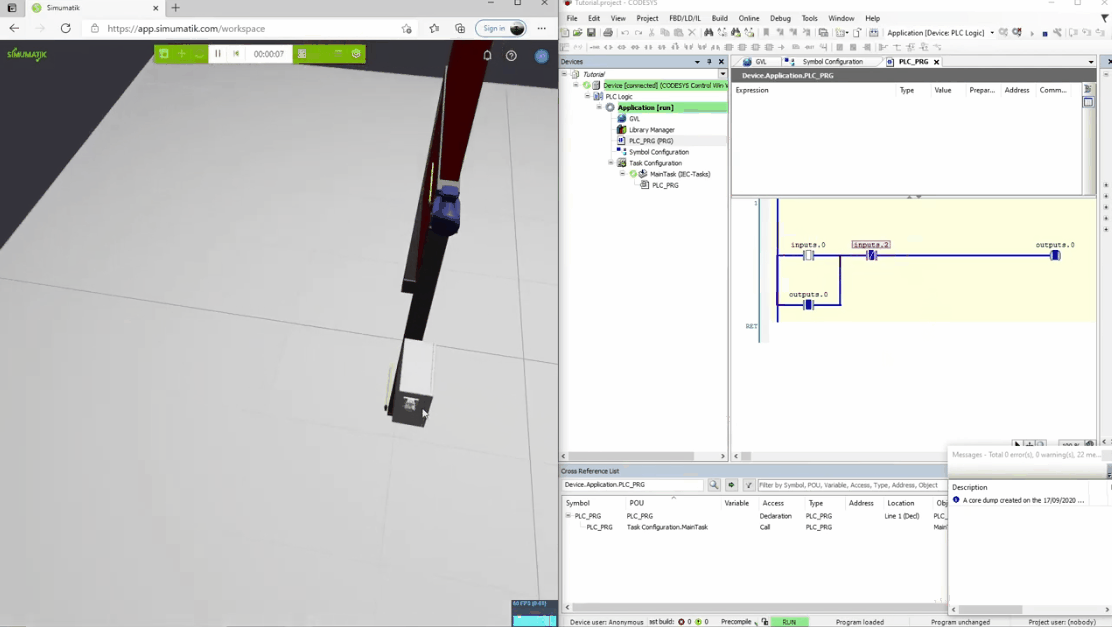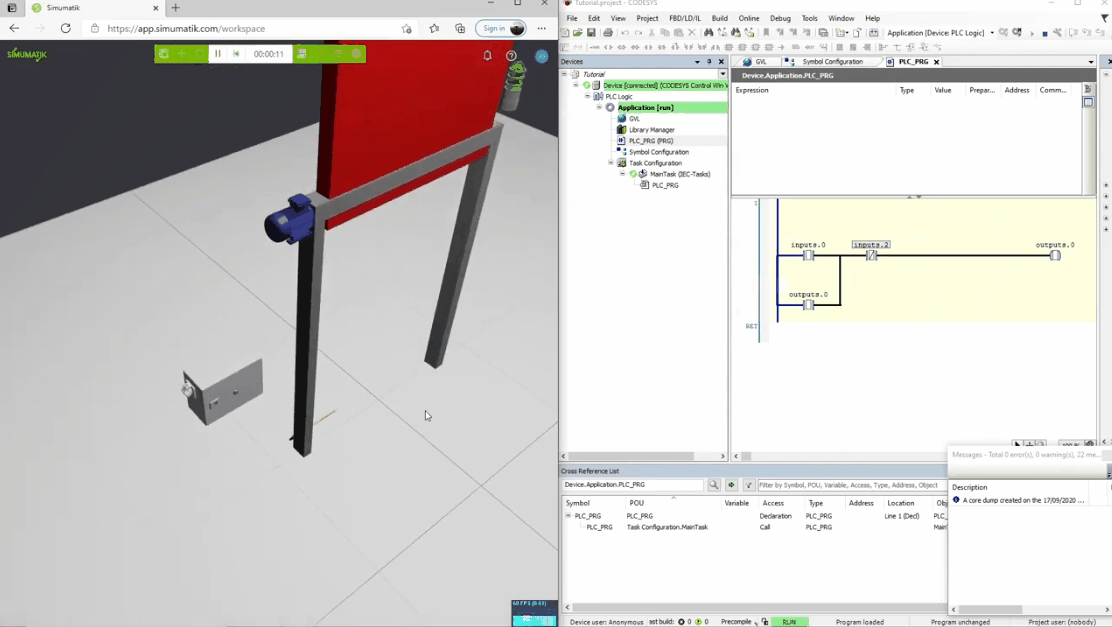
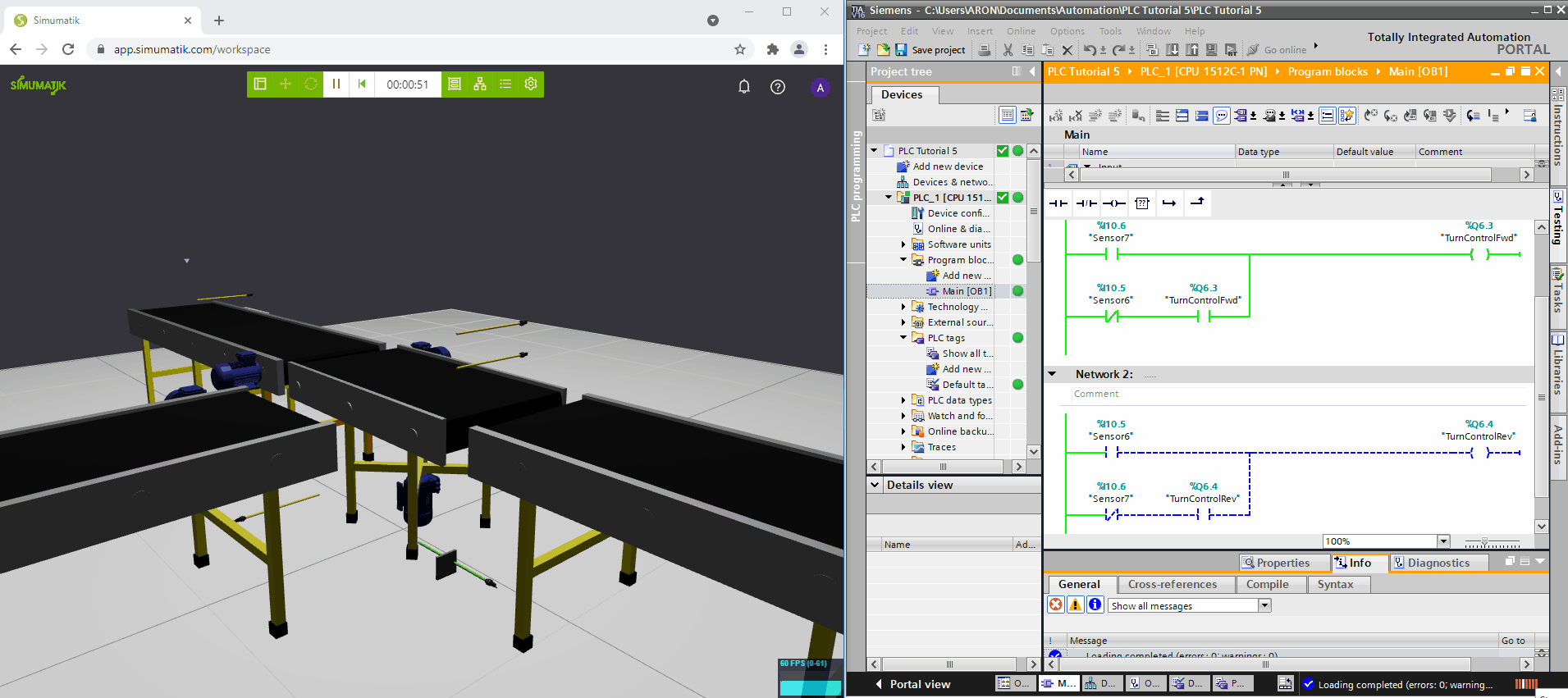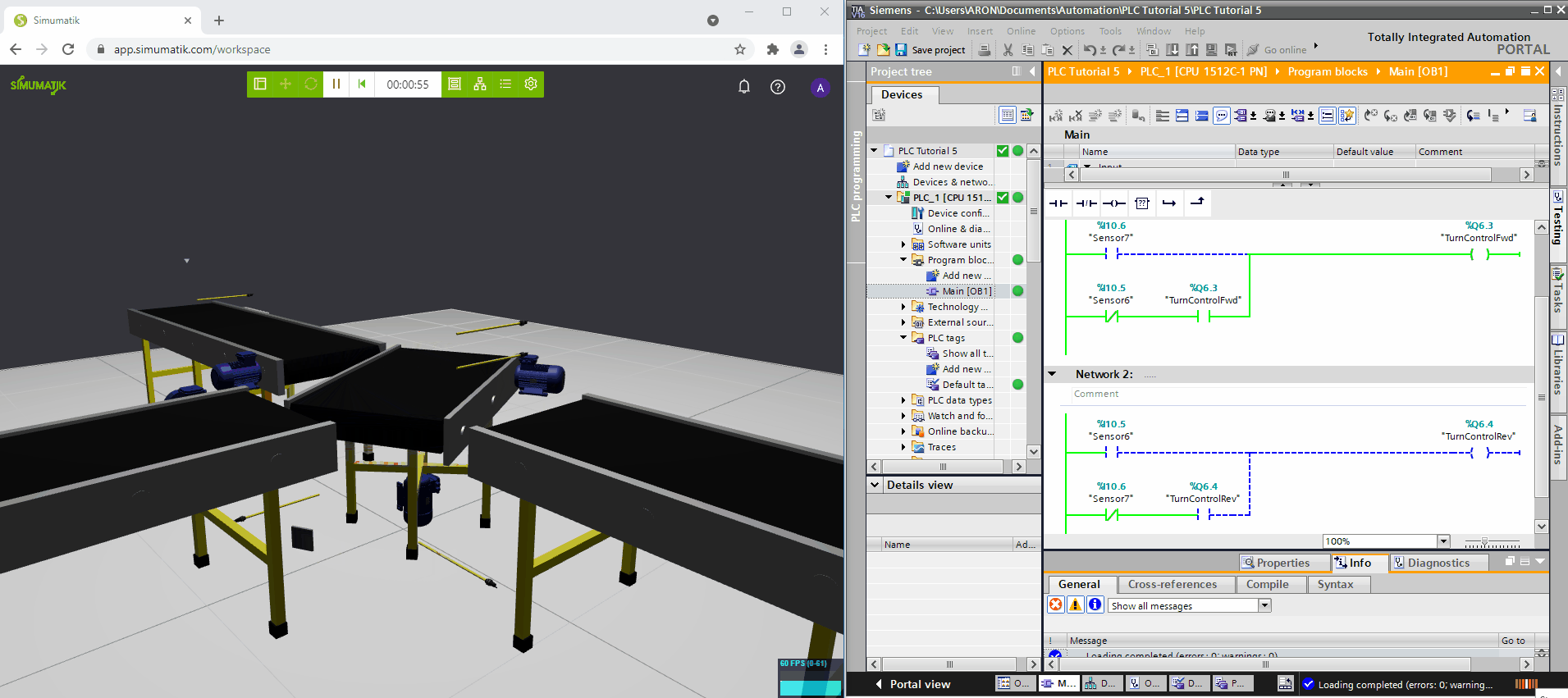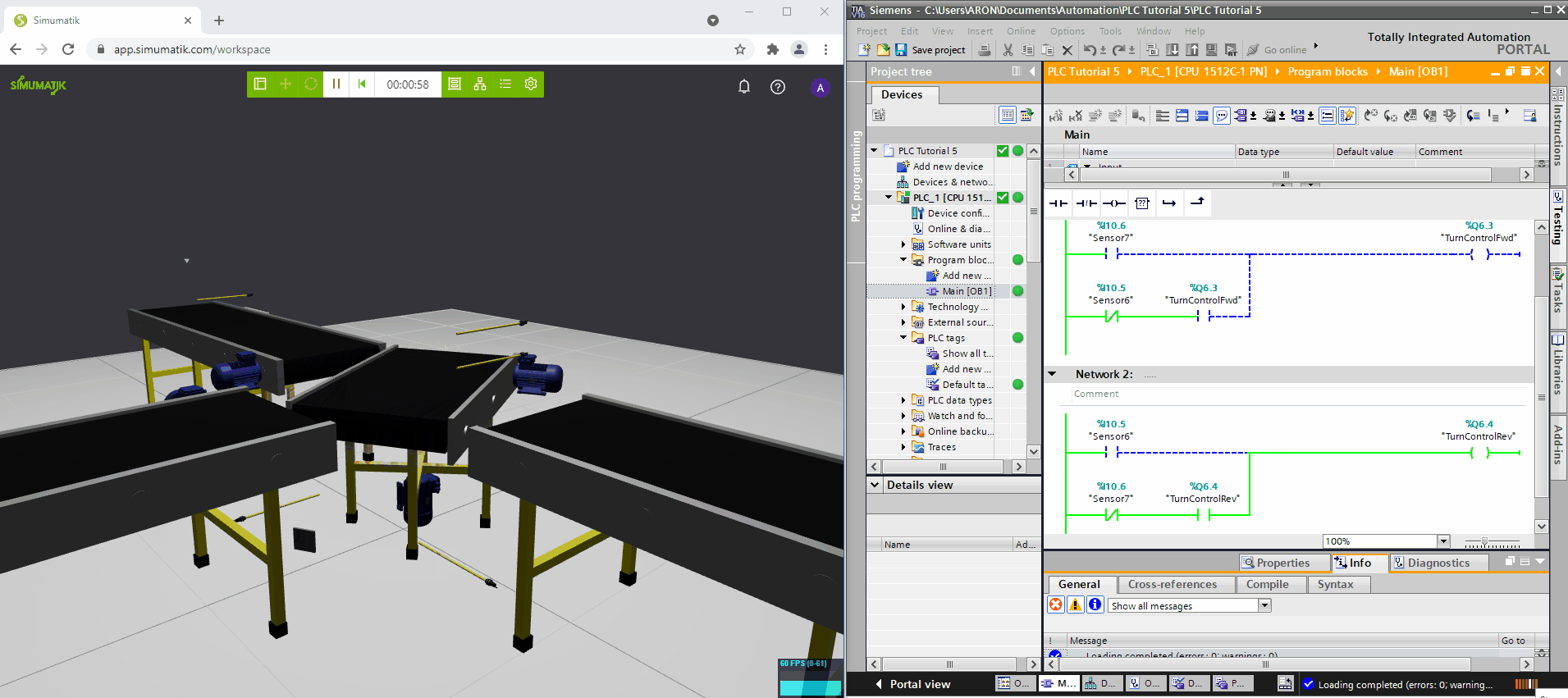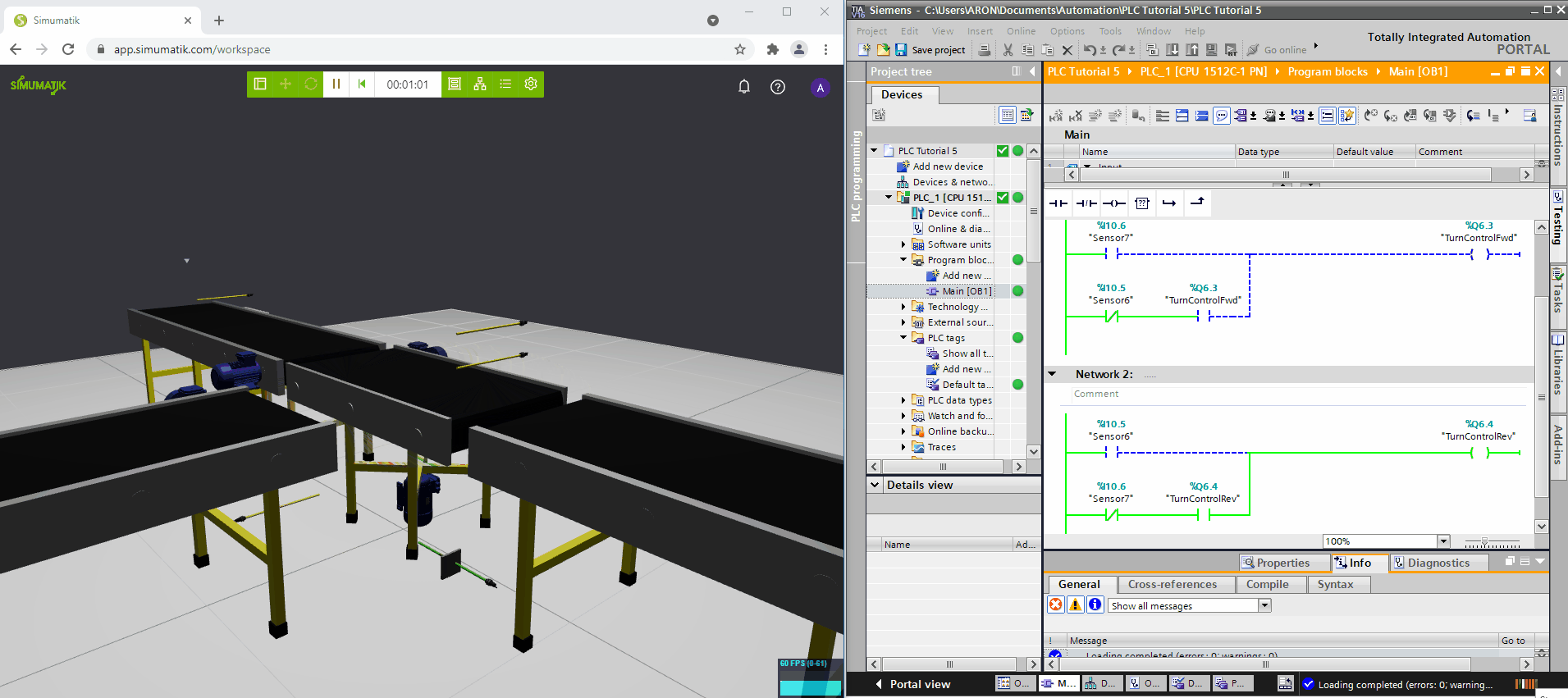
In the gifs below three different Simumatik models are connected to three different PLC systems (Codesys, Siemens TIA Portal, and Beckhoff TwinCAT3) and one Simumatik model to a robot system (Fanuc Roboguide). In these different cases, the control system logic is shown next to the Simumatik model. By using a Simumatik model together with a PLC or a robot controller, the programmer can test the logic of the system towards the virtual environment. This can be done in the early stages of the programming phase in the automation project, which enables to make test-driven decisions even though the real system does not need to be accessed.
Codesys
Siemens TIA Portal
Beckhoff TwnCAT3
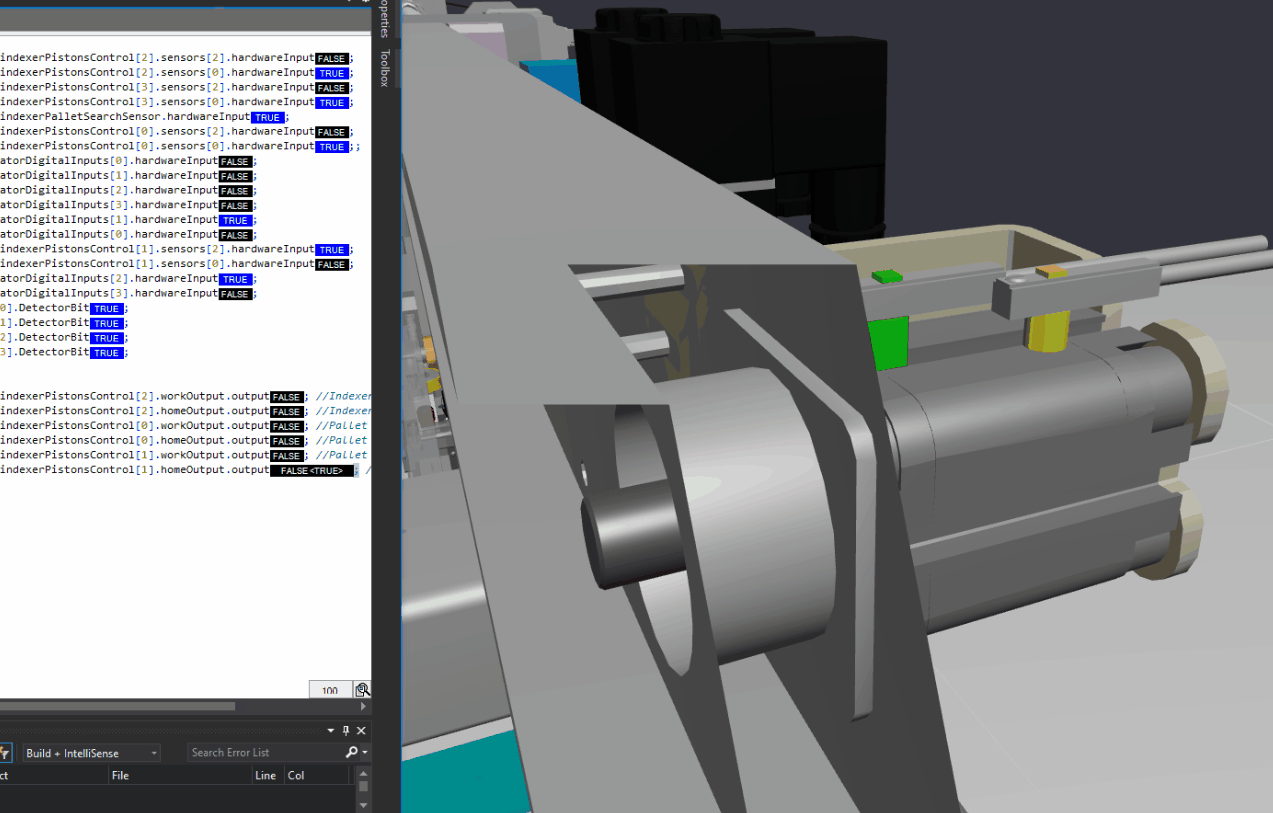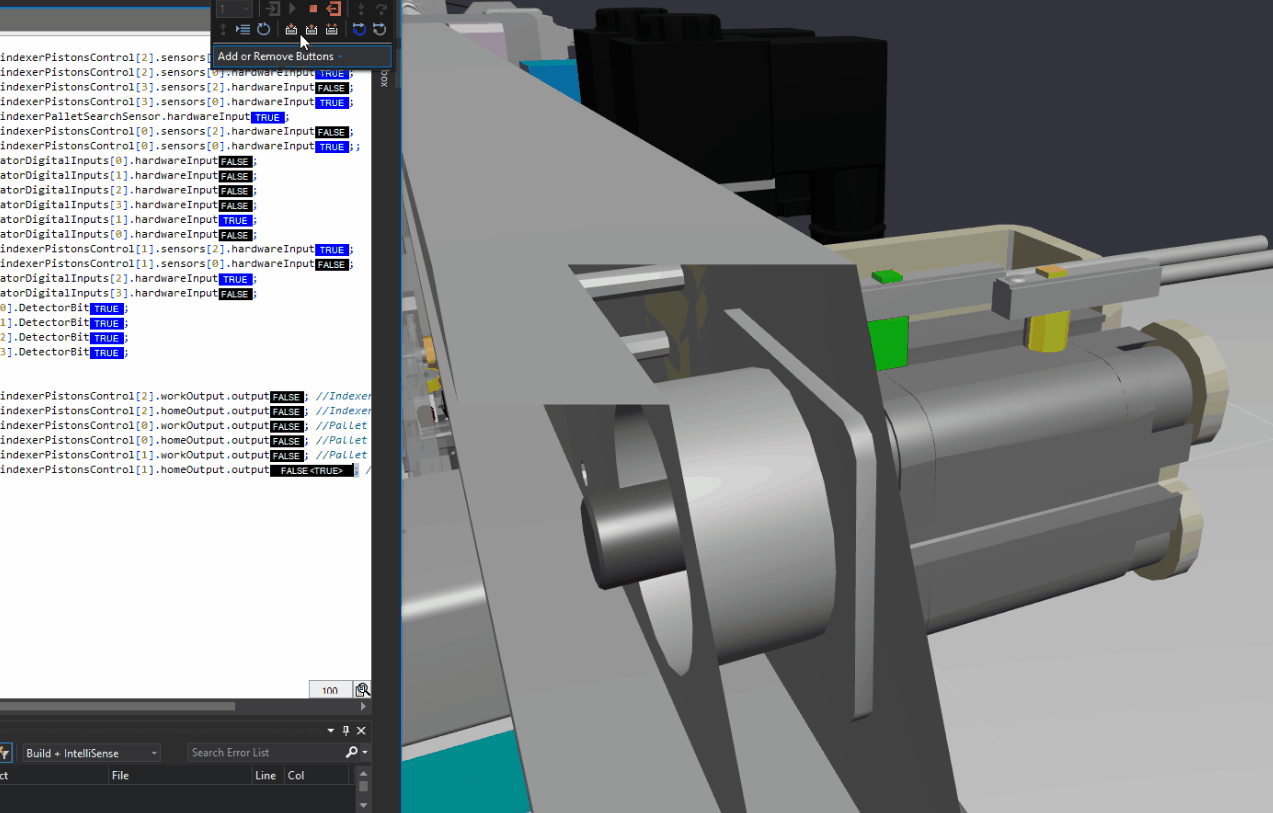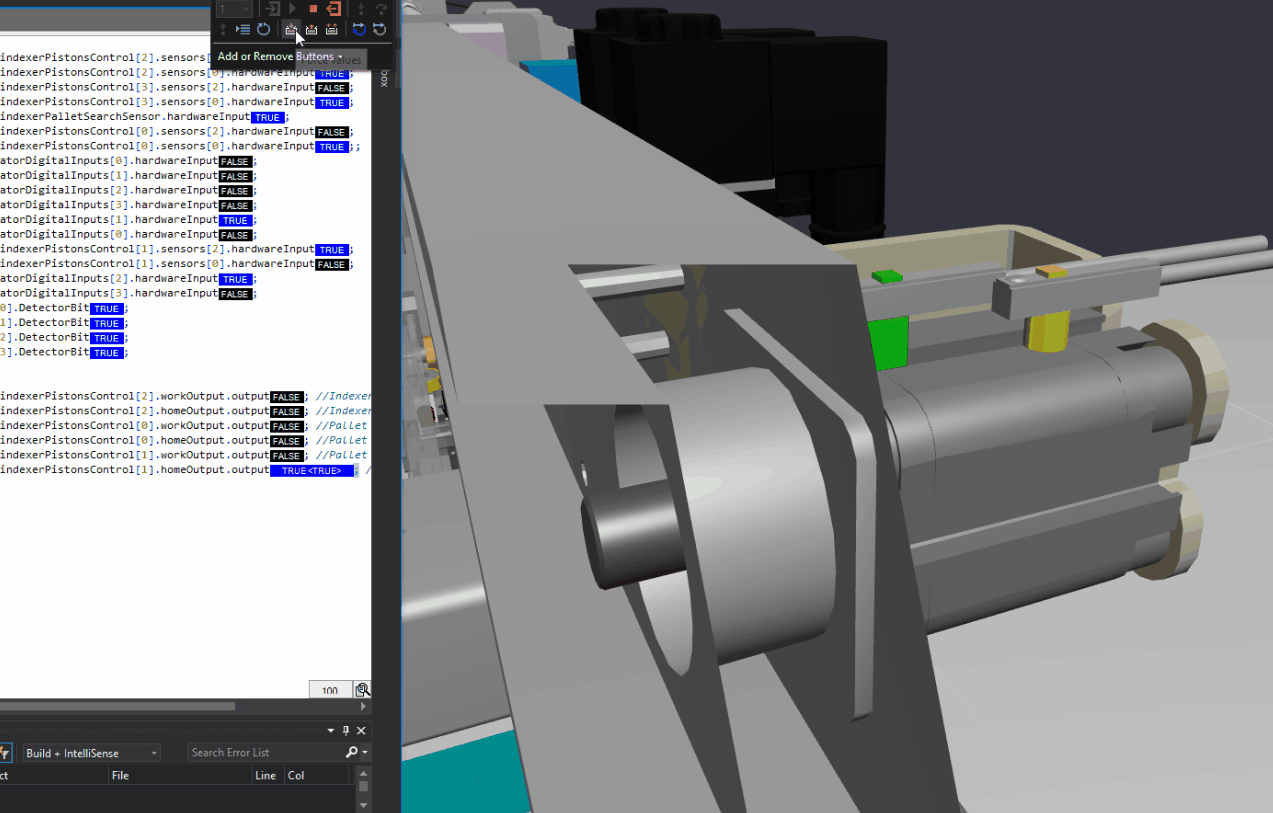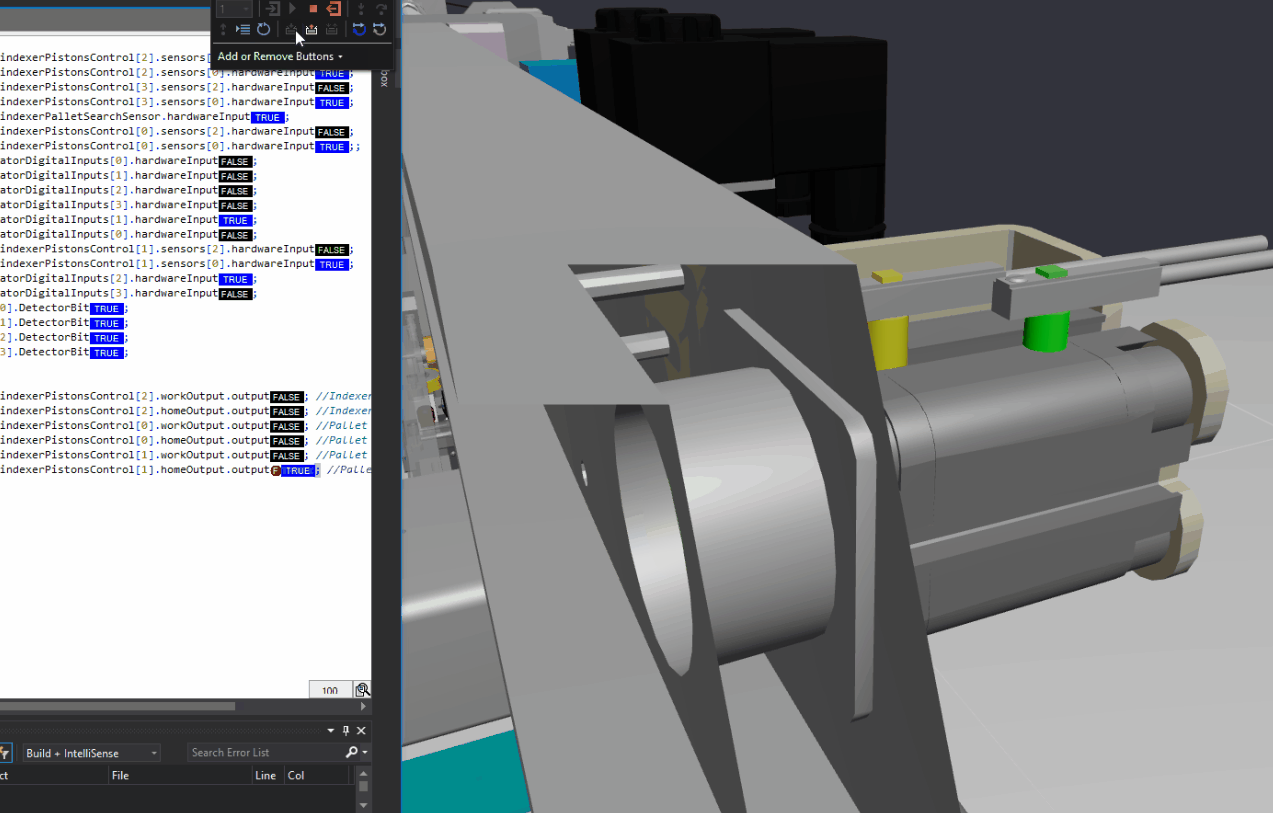
FANUC Roboguide
Industrial applications
A Simumatik model is not only for virtual commissioning, but can also be applied for Retrofitting, Energy optimization and Operator Training.
Virtual Commissioning
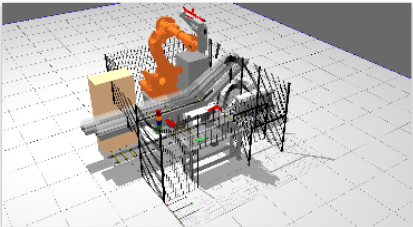
Refers to the process of checking, inspecting, and testing every component of the system, individually and as a system or subsystem.
Retrofitting
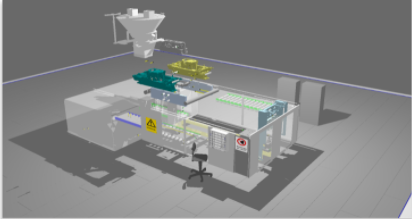
Refers to utilize a digital model of an existing system that will be changed, often with short commissioning slots. Using Simumatik for Virtual Commissioning during a retrofit project enables having a tested control system beforehand.
Energy Optimization
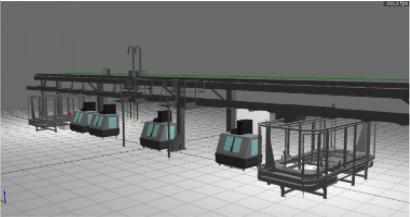
By using a Simumatik model of a system, calculations of energy utilizing can be performed, enabling the control system to be tuned for energy optimization
Training
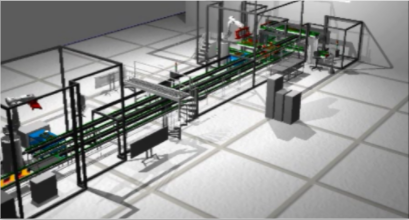
The Simumatik model can be used to train operators for different scenarios in a new or existing system.
Educational applications
By using Simumatik in education the students get direct access to technology, reduces requirements for physical resources and creates new opportunities for distance learning.
Copyright © 2026

